IDO GREENBERG
(updated: July 2021)
|
I am a researcher in the areas of
Algorithms, Data Science and Mathematical Modelling, looking to face
challenges of both intellectual and practical importance, along with
world-class research scientists. My great passion is to gain and
simplify knowledge, spread it and apply it to new
fields, pushing the limits of both understanding and capability. Currently I am particularly
interested in fundamental research and better understanding of Machine
Intelligence and Deep Neural Networks. •
Talpiot graduate •
MSc from TAU in applied math (summa
cum laude, excellence reward of math school, 2 journal publications) •
Experience in ML and data-science (Google, Istra, Technion) and operations
research (MAFAT) |
||||
Software
|
Applicational Field |
Title |
Year |
Language |
Code |
Description |
|
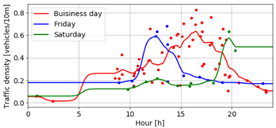
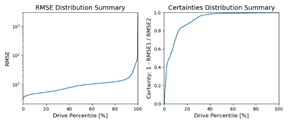
Traffic analysis |
Traffic
Analysis in Original Video Data of Ayalon Road |
2019 |
Python |
The
recording smartphone in action Out-of-the-box
SSD vs. the dedicated detector Probabilistic
field of the expected next-location of a tracked
vehicle Traffic
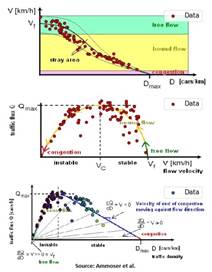
density is indeed high in known rush-hours The fundamental
traffic diagram (density, speed and flux):
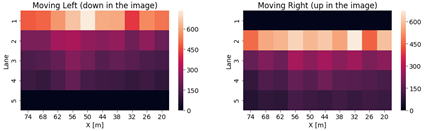
practice vs. theory Lane
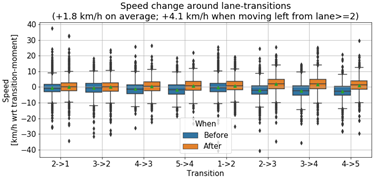
transitions mostly occur on the right lanes Left lane
transition is followed by average speed increase of 4.1 km/h |
|
|
News |
Scraping
and Analysis of Hebrew Newspapers |
2019 |
Python |
summary
of data parties
and politicians count graph
embedding of words by context-similarity |
|
|
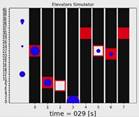
Elevators |
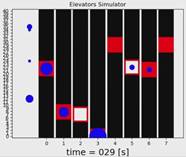
Elevators
Simulator |
2018 |
Python |
Elevators
continuous-time visual simulator, intended to test various algorithms for
elevators managing. visual
simulation single scenario
summary multi
scenario summary |
|
|
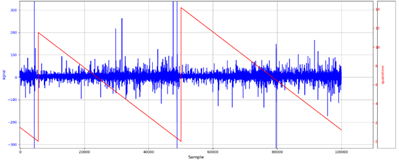
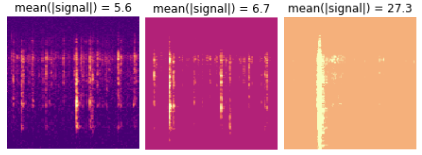
Earthquakes |
[Kaggle]
Earthquake Prediction |
2019 |
Python |
Prediction of the
remaining time until next earthquake according to seismic measurements. Worked in the framework
of a Kaggle
competition with prizes of 50K$, as part of a silver-medal winning
team that included Zahar Chikishev (full time)
and myself (part time). The repo includes only my
work, mainly concentrating on two Neural-Network solutions based on
raw-signal:
seismic
signal and corresponding time-until-next-quake a sample
of mel-spectrogram images |
|
|
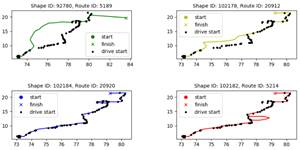
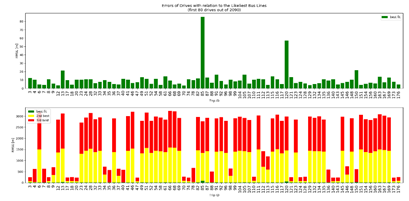
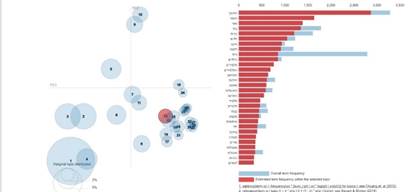
Public transportation |
[Hackathon]
Matching of Recorded Bus Trips to Planned Routes |
2019 |
Python, C++ |
This project was
developed in collaboration with Oded Shimon during the two-days Civil
Hackathon of the Israeli Workshop of Public Knowledge. Both data sets of
planned bus routes and of actual bus trips are publicly available in Israel,
allowing diagnosis of trips and comparison of their timings and routes to the
plans. However, it is suspected
that the reported matching between the planned routes and the actual trips is
inaccurate, making any diagnosis ineffective. This project shows that
within limited subsets of the data, all the observed trips correctly
correspond to their reported route. It also provides general
tools for detection of uncertainly-classified trips
(with more than one plausible planned route) and of anomalous trips (with no
plausible planned route). The match of a trip to a
planned route is essentially calculated through the distances of the observed
trip locations from the route. a trip
vs. several potential routes best
route fits vs. 2nd and 3rd best fits anomality
and certainty distributions of trips |
|
|
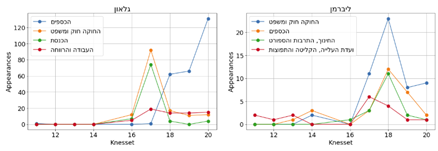
Knesset committees
protocols |
[Hackathon]
Analysis and Clustering of Hebrew Knesset Committees Protocols |
2019 |
Python |
This project was carried
out as part of Talpiot-alumnus single-day hackathon with a group of 6 members
under supervision of the Israeli Workshop of Public Knowledge. In order to improve the
public access to the extensive parliamentary activity carried in the Knesset
committees, the corresponding protocols were studied
and some relevant information was extracted regarding both the maturity of
the data and the information it carries. In addition, several
topic-based clustering approaches were tried, showed promising potential and yielded several results until the end of the
hackathon. quantification
of the parliamentary activity of a sample of Knesset members visualization
of LDA-based clustering (circle = cluster of protocols) |
|
|
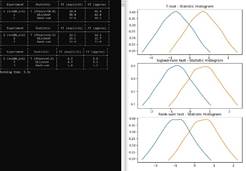
Statistics |
Numeric
Calculation of Fisher Information for Quantification of Information Loss in
Non-Parametric Tests in Two-Populations-Comparison |
2018 |
Python |
Non-parametric
statistical tests can avoid the data-normality assumption in the cost of
losing some of the information in the data. NumericFI module quantifies the loss of
information in non-parametric tests (signed-rank & rank-sum, both often
named Wilcoxon test) compared to parametric tests (t-test) in the case of two
paired datasets of normal iid data, using numeric calculation of Fisher
Information of each test statistic. The calculations show
that while the t-test does have some advantage, it is quite minor (less than
10% in terms of Fisher Information, which roughly means it can be compensated
by using 10% more data). In addition, the signed-rank test looks slightly better
than the rank-sum test. These results are consistent with literature that
studied such tests efficiency using different approaches. output
example |
|
|
Signal processing |
Spectrum
reconstruction for signals with dropped samples |
2019 |
Python |
Given a signal sampled
in discrete uniform times up to certain missing points, this module compares
various methods to find the Fourier spectrum of the original signal and
reconstructs the missing points. It is shown that
ignoring the missing points causes major disturbances to the Fourier
transform, and the limited tests that were tried, linear reconstruction of
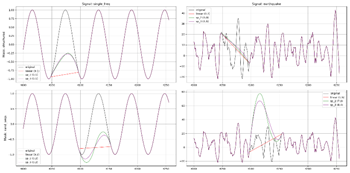
the signal seems like the best way to prevent these disturbances. demonstration
of the interpolation-based methods |
|
|
Signal processing |
ICA-based
Sound Decomposition |
2019 |
Python |
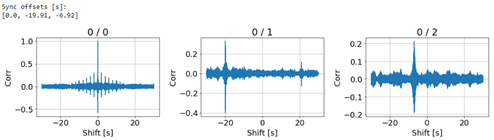
Synchronization of the
start-times of Under most setups,
the process failed to cleanly reconstruct the original components from which
the recorded sounds consisted. a sample
of convolutions used for signals-synchronization |
|
|
Finance |
Long-Term
Savings Calculator |
2018 |
Python |
Main functions: Generic tools:
Generic tools:
WARNING: nothing is guaranteed to be
(even approximately) correct. WARNING: validity of calculations is
probably restricted to Israel. output
example |
|
|
Plotting infrastructure |
Interactive
Plotter |
2018 |
Python |
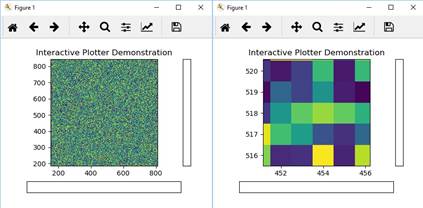
Infrastructure for
interactive figures, in which the limits of the axes are changed dynamically
by scrolling and dragging the mouse. zoom out
vs. zoom in |
|
|
Graphical interface infrastructure |
Window
Controller |
2018 |
Shell |
Move and resize active
window programmatically (Linux only; intended to be used along with
corresponding customized keyboard shortcuts). |
Academic Publications
|
·
Noise Estimation Is Not Optimal: How to Use
Kalman Filter the Right Way Ido Greenberg, Netanel Yannay,
Shie Mannor Abstract: Determining the noise parameters of
a Kalman Filter (KF) has been studied for decades. A huge body of research
focuses on the task of estimation of the noise under various conditions,
since precise noise estimation is considered equivalent to minimization of
the filtering errors. However, we show that even a small violation of the KF
assumptions can significantly modify the effective noise, breaking the
equivalence between the tasks and making noise estimation an inferior
strategy. We show that such violations are very common, and
are often not trivial to handle or even notice. Consequentially, we argue
that a robust solution is needed – rather than choosing a dedicated model per
problem. To that end, we apply gradient-based
optimization to the filtering errors directly, with relation to a simple and
efficient parameterization of the symmetric and positive-definite parameters
of KF. In radar tracking and video tracking, we show that the optimization
improves both the accuracy of KF and its robustness to design decisions. In
addition, we demonstrate how an optimized neural network model can seem to
reduce the errors significantly compared to a KF – and how this reduction
vanishes once the KF is optimized similarly. This indicates how complicated
models can be wrongly identified as superior to KF, while in fact they were
merely more optimized. ·
Detecting Rewards Deterioration in Episodic
Reinforcement Learning Ido Greenberg, Shie Mannor ICML, 2021 Abstract (informal): In Reinforcement Learning (RL),
where an agent is trained to do tasks in a certain environment (e.g.
autonomous driving, medical devices, etc.), the agent performance may
deteriorate due to various reasons (e.g. changes in the environment). Certain
works address training under changing conditions, but in production training
is often forbidden: when your car behaves
suspiciously with a passenger sitting inside, you don’t begin to retrain the
car! Rather, you wish to detect the performance deterioration ASAP, and
activate safety & fallback mechanisms. Our work addresses the detection of
performance degradation in episodic RL. This is essentially a statistical
problem for mean-shift detection in the rewards of the agent. However, the
non-i.i.d nature of the rewards makes many common
statistical tests irrelevant for the problem. Instead, we use the episodic
structure of the signal to formulate the problem as multivariate
mean-shift detection. That is, given K episodes of T time-steps each, we consider the 1D
sequence of length KT by a T-dimensional sequence of length K, in which the copies in the
sequence are i.i.d. Then we suggest a
concrete deterioration model which allows us to derive an optimal test for
detection of deterioration. We also show how to control the False Alarm
Rate of the test, even when running it sequentially on non-i.i.d data. Finally, we show that indeed, our
test detects deterioration in experiments significantly faster and with
higher probability compared to alternative tests. ·
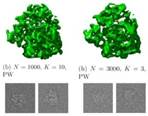
Common Lines Modeling for Reference Free
Ab-Initio Reconstruction in Cryo-EM Ido Greenberg, Yoel Shkolnisky Journal of Structural Biology, 2017 Abstract (informal): Reconstruction of molecular
structures (e.g. proteins) is essential for understanding of their biological
function. Such reconstruction from images of electron-microscope requires
estimation of the unknown viewing directions of the images. Common lines
between the images reveal the relative viewing direction between any pair of
images, but extremely low SNR often leads to errors in the detection of the
common lines. This research attempts to detect the
reliable estimates of the common lines, in order to
increase their weight in the estimation of the images' viewing directions.
This new feature, incorporated into an existing reconstruction algorithm, is
shown to achieve improvement of ~40% in the resolution of the reconstructed
map of a ribosome's subunit. ·
A Graph Partitioning Approach to Simultaneous Angular
Reconstitution Gabi Pragier, Ido Greenberg, Xiuyuan Cheng, Yoel Shkolnisky IEEE Transactions in Computational Imaging,
2016 Abstract (informal): Reconstruction of molecular
structures (e.g. proteins) is essential for understanding of their biological
function. Such reconstruction from images of electron-microscope requires
estimation of the unknown viewing directions of the images. The viewing directions
(denoted This part of the process can be
summarized as follows:
In this paper we locally estimate
the consistency of distortion between certain relative directions, form these
estimated relations as a graph, and use spectral analysis of the graph to
synchronically aggregate all the local estimations in favor
of a global partition of We use simulations of
electron-microscope images to demonstrate that using this method as part of
the reconstruction algorithm significantly improves the reconstruction. |
Articles and Presentations
|
All the materials below are free to
use for any purpose as long as proper attribution is
given. The writer has
no official education or certification in most topics appearing below. None
of the documents is meant to recommend any action to the reader, and no
responsibility on such actions will be taken. |
|
|||||||||
|
Field |
Topic |
Framework |
Year |
Documents |
Language |
Pages |
Short summary included |
Comments |
|
|
Mathematical Modeling |
Elevators
Waiting-Time Optimization |
MSc course |
2014 |
HE |
- |
- |
|
||
|
Simulator:
Liquid within Moving Container |
High school |
2007 |
HE |
49 |
Yes |
In collaboration with Jonathan
Cederbaum |
|||
|
Machine Learning |
Web
Servers Classification |
High school |
2008 |
HE |
42 |
Yes |
In collaboration with Jonathan
Cederbaum and CheckPoint Security |
||
|
Illustrated
List of Basic Methods in ML |
Independent |
2018 |
EN |
- |
- |
Illustrations were collected from various
sources (none was made by me) |
|||
|
Intro
to Deep Reinforcement Learning |
Independent |
2021 |
PPTX* |
EN |
13 |
- |
|
||
|
Finance |
Basic
Concepts in Finance and Investments |
Independent |
2017 |
HE |
12 |
Yes |
|
||
|
Pension
Tutorial |
Independent |
2018 |
HE |
20 |
Yes |
|
|||
|
Human Resources |
Disturbing
Factors for Technological Employees in Permanent Military Service |
Independent |
2017 |
HE |
4 |
No |
Based on survey among 21 subjects |
||
*PPTX files are
partially corrupted until I find an alternative hosting to Google Drive.
Self-studied Courses Summaries
|
All the materials below are free to use
for any purpose as long as proper attribution is
given. Most summaries
passed little to none review, and probably contain inaccuracies. |
|||||||||
|
Field |
Topic |
Framework |
Year |
Documents |
Language |
Pages |
Short summary included |
Main source |
|
Algorithms |
Basic
algorithms, graphs, DP, LP, spatial search, etc. |
Independent |
2018 |
EN |
14 |
No |
Algorithms
1, Technion, 2013
and analog courses in TAU, HUJI and Udacity |
|
|
Information |
Information
Theory |
Independent |
2019 |
EN |
22 |
Yes |
Information,
Physics and Computation,
Stanford, 2009; Elements of Information Theory, 2006 |
|
|
Signal processing |
Digital
Signal Processing |
Independent |
2018 |
EN |
13 |
No |
||
|
Graphs |
Intro
to graph theory, basic algorithms, spectral graph theory and SNA |
Independent |
2019 |
EN |
16 |
No |
Distributed sources (see references within the PDF) |
|
|
Random
Graphs |
PhD course |
2021 |
EN |
|
No |
Random Graphs and Hypergraphs (049014), O. Bobrowski, Technion,
2021 |
||
|
Statistics |
Intro
to Statistical Theory |
Independent |
2018 |
EN |
11 |
No |
||
|
Cointegration |
MSc course |
2015 |
HE |
- |
- |
Distributed sources |
||
|
Advanced
Statistical Theory |
Independent |
2019 |
EN |
25 |
Yes |
|||
|
Experimental
Design and Analysis of Variance |
Independent |
2018 |
HE |
16 |
Yes |
Notes by prof. David Steinberg, TAU (syllabus) |
||
|
Probability
in High Dimension |
PhD course |
2020 |
EN |
11 |
Yes |
Distributed sources (see references within the PDF) |
||
|
Statistical
Learning Theory |
Independent |
2021 |
EN |
4 |
No |
Distributed sources (see references within the PDF) |
||
|
Optimization |
Convex
optimization |
Independent |
2019 |
Was not
summarized |
- |
- |
- |
|
|
Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning |
Theoretical
Intro to ML |
Independent |
2019 |
Was not
summarized |
- |
- |
- |
67577:
Introduction to Machine Learning, Shai Shalev-Shwartz, HUJI |
|
Intro
to Artificial Intelligence |
Independent |
2016 |
EN |
47 |
Chapters
summaries +
summarizing table |
Udacity
(Sebastian Thrun, Stanford & Google) |
||
|
Intro
to Supervised Learning through Linear Regression |
Independent |
2018 |
EN |
- |
Summarizing
table on last
slide |
Distributed sources |
||
|
Supervised
Learning |
Independent |
2016 |
EN |
17 |
No |
Udacity (Georgia Tech) |
||
|
Unsupervised
Learning |
Independent |
2017 |
EN |
14 |
No |
Udacity
(Georgia Tech) |
||
|
Reinforcement
Learning |
Independent |
2018 |
EN |
16 |
Yes |
Udacity
(Georgia Tech) |
||
|
Machine
Learning (only
complementary materials on top of previous courses) |
Independent |
2017 |
EN |
10 |
No |
Coursera (Andrew
NG, Stanford) |
||
|
Intro
to Machine Learning (only
complementary materials on top of previous courses) |
Independent |
2018 |
EN |
3 |
- |
Udacity
(Sebastian Thrun, Stanford & Google) |
||
|
Intro
to NLP |
Independent |
2017 |
EN |
23 |
Chatbot-oriented
summary |
NLTK
book (O’Reilly Media Inc.) |
||
|
Intro
to Deep Learning |
Independent |
2019 |
Was not
summarized |
- |
- |
- |
Udacity
(Facebook) CS231n: CNNs (Stanford) |
|
*PPTX files are
partially corrupted until I find an alternative hosting to Google Drive.
Other
Stuff
|
·
Winds of Winter: all public sample chapters in one
printable document. ·
Track & Field: my personal
page in the Israeli Athletic Association (all 800m results were
mysteriously lost ☹). |